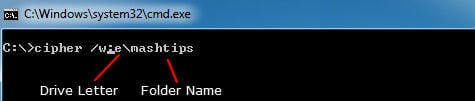
Microsoft says, When you delete files or folders, the data is not initially removed from the hard disk. Instead, the space on the disk that was occupied by the deleted data is “deallocated.” After it is deallocated, space is available for use when new data is written to the disk. Until space is overwritten, it is possible to recover the deleted data by using a low-level disk editor or data-recovery software. We advise you whenever you delete sensitive files from your PC, make sure those are deleted properly and can’t retrieve in future. There are a couple of tools to safely delete files, but Windows is coming with an inbuilt tool to do this job for you. The cipher.exe command is an external command that can be used to overwrite on your free hard disk space to permanently delete your deleted file from hard disk. We are using this command to overwrite data that you have deleted so that it cannot be recovered and accessed. Please follow the steps below to overwrite deleted data on your hard disk by using Cipher.exe, use the /w switch with the cipher command. Close all open applications before proceeding. Click on Start, click Run, type cmd, and then press ENTER. Type cipher /w:driveletterfoldername, and then press ENTER. Replace the drive letter with your hard disk drive letter and specify the folder name. Please see the screenshot below with a sample command. This drive letter is E and the folder name is mashtips in this case.
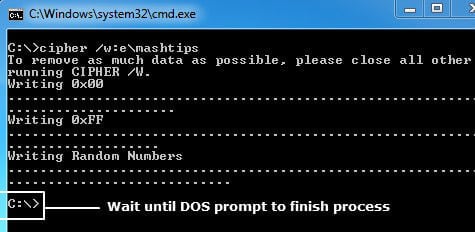
Once you enter the command, the system will start to write 00 (0000 0000) on all empty or deleted space of that volume. In the second level, the tool will write FF (1111 1111) on the same place. And as the last step, it will write the Random Numbers over it, to make sure the deleted files are non-recoverable.
Please wait until you get the DOS prompt again to make sure the process finished. This command permanently removes the deleted data from the hard disk and can take a long time if you are overwriting a large space Hard Disk.
Δ